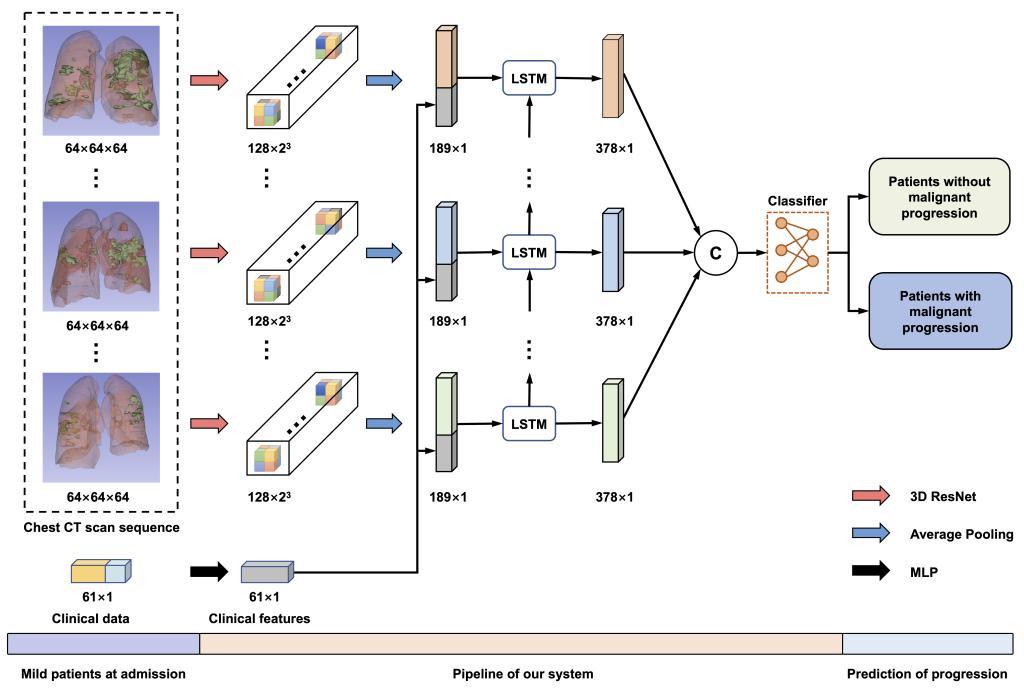
新冠肺炎具有高传染性,在疫情爆发地区,许多患者同时涌入医院给公共医疗系统带来巨大压力。治疗优先级通常取决于首次评估的病情严重程度。然而,临床观察表明,一些轻症患者可能会迅速恶化。因此,尽早识别出可能存在病情恶化的患者对优化治疗策略至关重要。本文开发了一个基于深度学习的早期预警系统,以预测新冠肺炎患者的恶性进展。该方法利用患者的CT扫描和门诊临床数据,在单中心研究中达到了0.920的AUC。本文还提出一种领域自适应方法,以改进模型的泛化性能,在多中心研究中达到平均AUC 0.874。该模型识别出了导致恶性进展的关键指标,包括肌钙蛋白、脑钠肽、白细胞计数、天冬氨酸转氨酶、肌酐和超敏C反应蛋白。
As COVID-19 is highly infectious, many patients can simultaneously flood into hospitals for diagnosis and treatment, which has greatly challenged public medical systems. Treatment priority is often determined by the symptom severity based on first assessment. However, clinical observation suggests that some patients with mild symptoms may quickly deteriorate. Hence, it is crucial to identify patient early deterioration to optimize treatment strategy. To this end, we develop an early-warning system with deep learning techniques to predict COVID-19 malignant progression. Our method leverages CT scans and the clinical data of outpatients and achieves an AUC of 0.920 in the single-center study. We also propose a domain adaptation approach to improve the generalization of our model and achieve an average AUC of 0.874 in the multicenter study. Moreover, our model automatically identifies crucial indicators that contribute to the malignant progression, including Troponin, Brain natriuretic peptide, White cell count, Aspartate aminotransferase, Creatinine, and Hypersensitive C-reactive protein.
论文地址:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1361841521001420?casa_token=hggarWmp9NIAAAAA:phdw0L2JVim7GwGaRvmusaZOGPr0LErUtaYg3ZYpTH6wjKLvffhoN36LXfmnGE4qgYsKhRCAKyE
代码地址:https://github.com/CongFang/PMP-COVID-19